

There is no need to learn these names and abbreviations.
Amino acid sequence chart code#
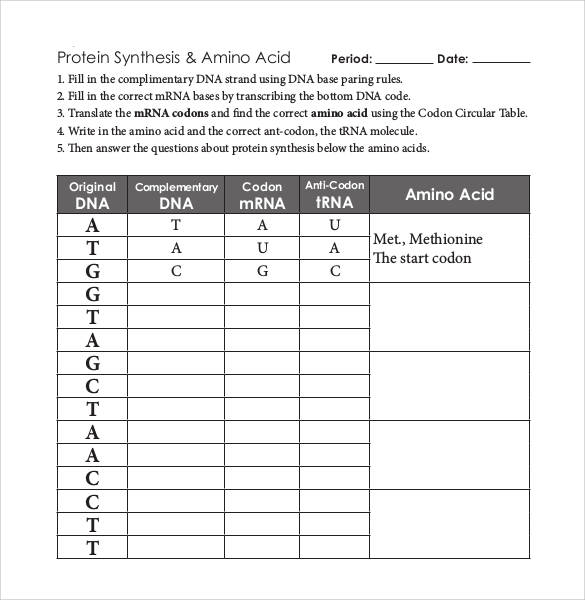
STOP codons cause transcription to terminate and do not code for an amino acid e.g. Appendix 3: List of amino acids and their abbreviations This table is included for reference only.The START codon initiates the process of transcription and ensure it starts in the right location (this is always the amino acid methionine in eukaryotic cells, coded for by the codon AUG) The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N) ( CHON ) in addition sulfur (S) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (Se) in the less common amino acid selenocysteine.Some send important signals to the transcription machinery.UGU and UGC both code for the amino acid cysteine.Organisms that are more closely related will share more common amino acid sequences in the cytochrome C protein. Relate amino acid sequences of cytochrome C from various species to genome evolution and protein function. This means that a change in the genetic code doesn’t necessarily result in a change in the amino acid sequence Compare and contrast amino acid sequences of cytochrome C in humans, other animals and bacteria.Carefully compare the sequences from left to right. Letters symbolize the amino acid they stand to. You will see the corresponding amino acid. Transcribed Image Text: Note: Focus on the amino acid sequence of the organism asked in this task. Find the third letter of the codon triplet in the box. Locate the intersect box of 1st row and 2nd column in the codon table. Find the second letter of the codon triplet from the upper axis of the table. Multiple mRNA codons can encode the same amino acid Find the first letter of the codon triplet from the left side of the table.The four bases found in RNA molecules (adenine, uracil, cytosine and guanine) have the ability to form 64 different codons.When comparing the genetic code to amino acid sequences, mRNA codons are often used.An anticodon is a sequence of three tRNA bases that are complementary to a codon.A codon is transcribed from the triplet and is complementary to it.A codon is a sequence of three mRNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid.A triplet is a sequence of three DNA bases that codes for a specific amino acid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
